Reconstructive Surgery for Left Orbital Defect Post-Mucormycosis
Overview
Mucormycosis, popularly referred to as the “black fungus,” is a rare but aggressive fungal infection caused by mucorales fungi. It primarily affects individuals with weakened immune systems, including those recovering from COVID-19. Following the pandemic, there was a noticeable surge in cases, especially in India. Globally, the incidence is estimated at 0.005 to 1.7 per million population, but in India, post-COVID-19, this shot up to over 14 cases per 100,000 population, making it an epidemic in itself.
In some severe cases, mucormycosis affects the eyes, leading to orbital invasion. According to Dr. Leena Jain, an acclaimed Plastic Surgeon in Mumbai:
“When mucormycosis progresses to the orbit, it often results in orbital exenteration — removal of the eye and infected surrounding tissues. This leaves behind a significant anatomical defect requiring surgical reconstruction for both function and appearance.”
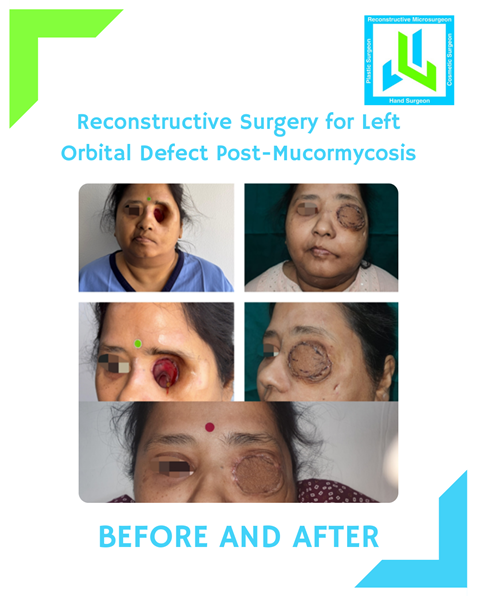
This case study highlights the journey of a 55-year-old woman who underwent reconstructive surgery for her left orbital defect caused by mucormycosis, performed by Dr. Leena Jain.
Basic Info
Clinic/Hospital Name: Plastikos Clinic / Lilavati Hospital
Patient’s Age: 55
Gender: Female
Patient Background
The patient, a 55-year-old woman, had a history of COVID-19 infection in 2021. During recovery, she developed mucormycosis, which rapidly progressed, affecting her left eye. To contain the infection and prevent it from spreading to the brain, surgical removal of the eye (orbital exenteration) was performed. Though life-saving, the procedure left her with a gaping defect in the orbit, continuous discharge, and emotional trauma due to facial disfigurement. Seeking functional rehabilitation and aesthetic restoration, she approached Dr. Leena Jain, a renowned specialist in complex facial reconstruction.
Symptoms
Patients with orbital defects post-mucormycosis often experience both physical discomfort and psychological distress. In this patient’s case, the following symptoms were observed:
Persistent discharge from the left orbital cavity
Open raw area in the orbit
Path of discharge tracking into the food pipe
Facial asymmetry
Loss of the eyeball and associated soft tissues
Crusting and infection in the orbital cavity
Difficulty in maintaining hygiene
Emotional distress and reduced confidence
Diagnostic Method
Detailed clinical examination of the orbital cavity
Evaluation of tissue condition and surrounding structures
Assessment for signs of recurrent infection
Determination of viability for flap coverage and reconstruction
Disease Diagnosed
The patient was diagnosed with a left orbital defect post-mucormycosis.
Dr. Leena Jain explains,
“After orbital removal, patients are left with a deep, unhealed cavity that not only causes persistent discharge but can also impact adjacent functions. This defect can become a source of chronic infection and social embarrassment. Hence, timely reconstruction is essential to restore both health and confidence.”
Treatment
To restore both form and function, the treatment plan involved a complex reconstructive procedure.
Pre-operative Preparation:
Infection control with antibiotics and antifungals
Nutritional optimization to promote healing
Pre-surgical imaging to map vascular supply
Psychological counseling and expectation setting
Step-by-Step Procedure:
Surgical Planning: A free flap reconstruction was selected to provide durable soft tissue coverage for the orbital cavity.
Wound Closure: The area was closed in layers to ensure optimal healing and symmetry.
Post Surgery Guidelines
After surgery, a set of clear guidelines was shared with the patient to ensure smooth recovery and long-term success:
Outcome
The patient achieved complete closure of the orbital defect. The discharge ceased, and no raw areas were visible. She no longer required daily dressings, significantly improving her comfort and confidence.
Long-Term Expectation
Following complete healing, the patient is eligible for an implant-based ocular prosthesis. This prosthetic eye will enhance her facial symmetry and allow her to regain a sense of normalcy. With continued follow-ups and proper care, long-term results are expected to remain highly satisfactory, both functionally and aesthetically.
Patient Feedback
“After I lost my eye, I felt like I had lost a part of my identity. I was constantly battling discomfort, discharge, and the emotional weight of looking different. Meeting Dr. Leena Jain changed everything. She not only treated me with care but also gave me hope. Today, my face looks whole again, and I no longer have to depend on dressings. I feel confident stepping out. I’m deeply thankful to Dr. Jain and her team for bringing back my smile.”